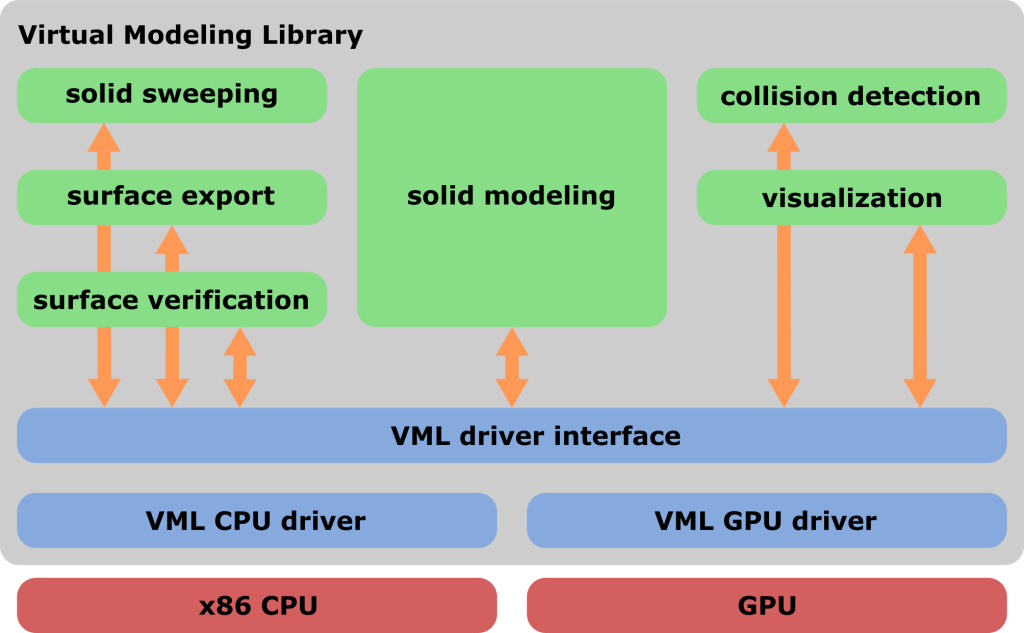
Virtual Modeling Library
PRECISE MODELING OF DETAILED GEOMETRIES FOR REAL-TIME SIMULATIONS

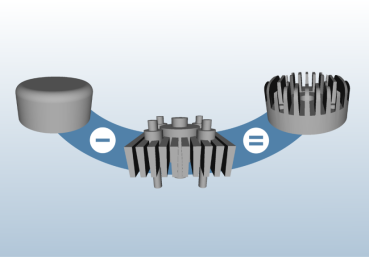
The Virtual Modeling Library (VML) is a software library that implements new algorithms for precise geometric modeling of solid bodies. It supports operations based on Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) as well as swept volume calculations. VML offers excellent scalability in terms of runtime and memory usage with respect to the number of modeling operations performed. This makes it ideal for industrial applications that demand both geometric accuracy and fast performance. A typical use case is the real-time simulation of material removal in machining processes involving a high number of operations.
In addition to modeling, VML includes algorithms for interactive visualization, collision detection between arbitrary geometries and the current geometry, and surface verification against a reference CAD model. To ensure high runtime efficiency, VML leverages the parallelization potential of modern hardware architectures, including multi-core CPUs and GPUs. Additional features include surface export of the current geometry and easy integration into other software systems.
The development of key components of VML was funded by the Regional Competitiveness Upper Austria 2007–2013 program through the European Regional Development Fund and the Province of Upper Austria.

Features
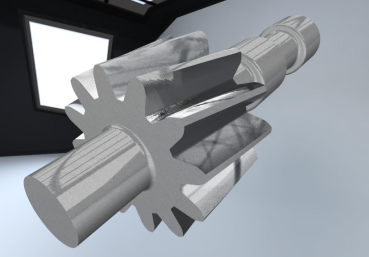
Solid Modeling: VML supports operations similar to Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG). Geometries must be provided as closed boundary surface models. A combination of hierarchical space partitioning and intelligent elimination strategies ensures high efficiency in both memory usage and runtime.
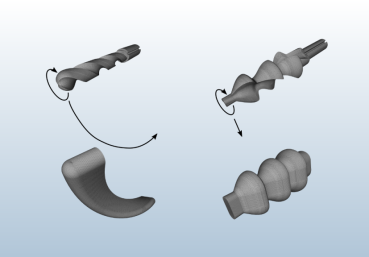
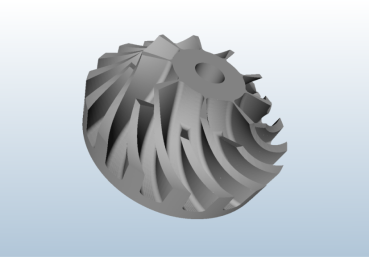
Swept Volume Calculation: VML computes the swept volume of a geometric object along a path using a point-cloud-based approach. Both the object and the path can be arbitrarily defined. The algorithm is highly efficient.
High Number of Operations: VML imposes no limits on the number of modeling operations. Even with 100,000 operations, memory and runtime performance remain efficient due to smart elimination strategies.
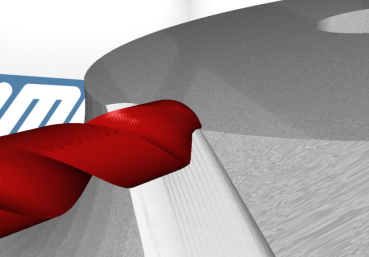
Collision Detection: VML detects collisions between the current model and any external geometry. Minimum distances can be defined. Collisions are identified in milliseconds thanks to spatial partitioning.
Surface Export: The surface of the current model can be exported as a triangle mesh with configurable resolution. Geometric details like edges and corners are preserved.
Interactive Visualization: VML offers a triangle mesh representation for real-time visualization. Using technologies such as OpenGL or DirectX, photorealistic rendering can be achieved.
High Accuracy: One of VML’s core strengths is its geometric accuracy. The result is never approximated—only final surface-contributing elements are retained, ensuring precision.
Dual Geometric Representation: VML supports both triangle meshes (fast, medium precision) and analytical surfaces (high precision, slightly reduced speed) to describe surface geometries.
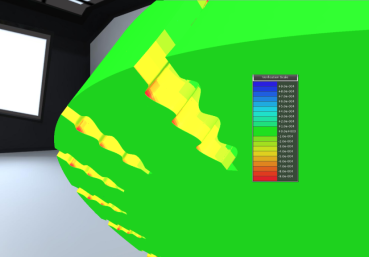
Surface Verification: VML compares the current model’s surface with a reference CAD model and computes differences in real-time. The difference is measured as the normal distance between surfaces.
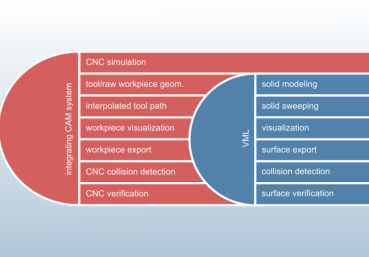
Easy Integration: VML features a compact API. CAM systems can use VML modules for modeling and swept volume calculation in machining simulations, and its collision and verification modules for CNC validation.
Ansprechperson

Dipl.-Ing. (FH) Alexander Leutgeb
Head of Unit Industrial Software Applications